Gut Microbiota, Leaky Gut & Metabolic Disorders: The Hidden Cascade
We're excited to share our latest review article published in Current Obesity Reports (2025):
“A Cascade of Microbiota-Leaky Gut-Inflammation—Is it a Key Player in Metabolic Disorders?”
Authored by Dr. Sidharth Mishra, Bryan Agadzi, Dr. Shalini Jain, and Dr. Hariom Yadav
🔗 Read the article
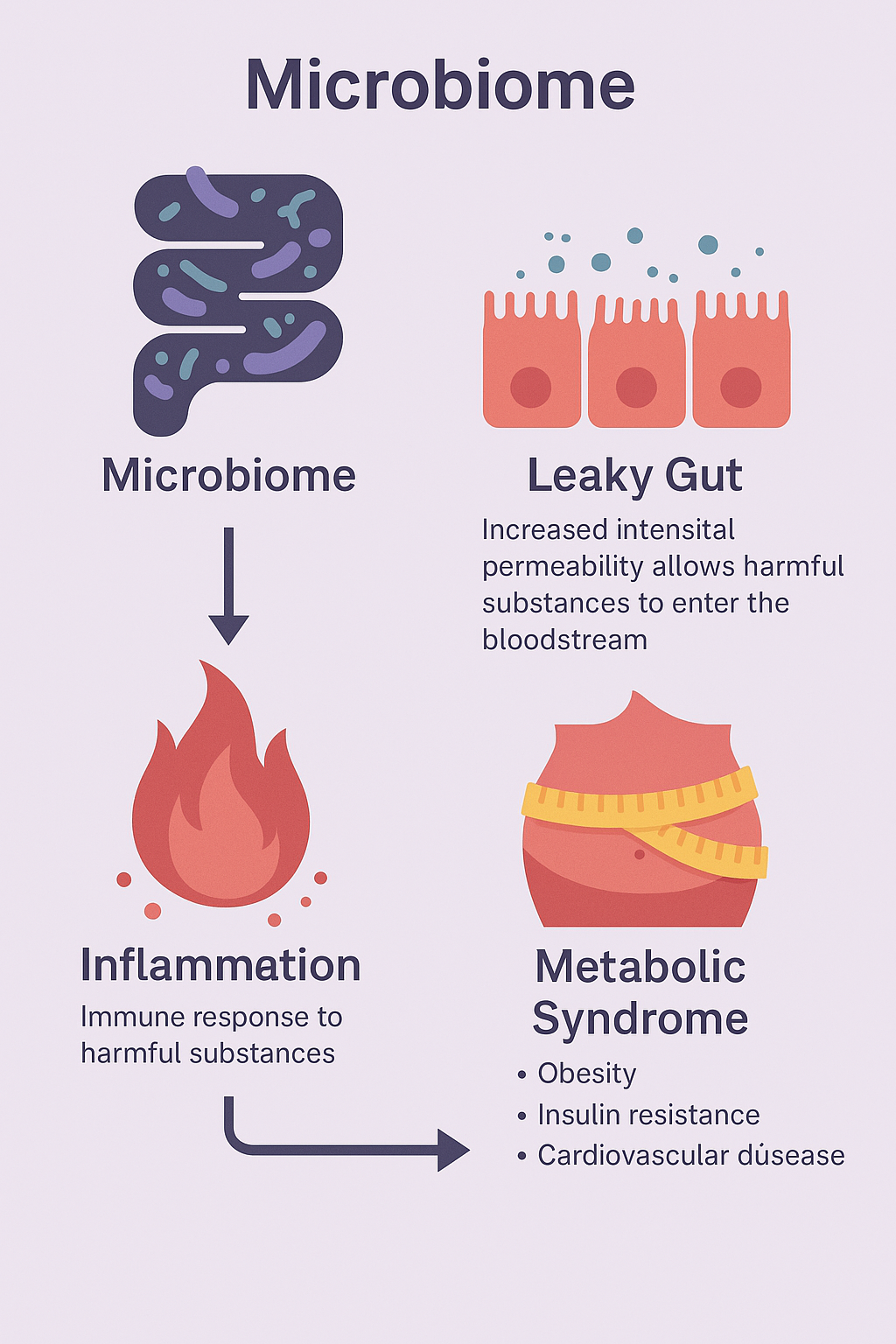
This comprehensive review was led by Dr. Yadav’s lab at the USF Center for Microbiome Research, and it explores how gut microbiota disturbances trigger a leaky gut, driving inflammation and systemic metabolic dysfunctions like obesity, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and even cognitive decline.
Why Leaky Gut Deserves Your Attention
Leaky gut, or increased intestinal permeability, allows harmful microbial byproducts (like LPS) to seep into the bloodstream. This triggers a condition called metabolic endotoxemia, leading to chronic low-grade inflammation—one of the key contributors to insulin resistance and the pathogenesis of multiple metabolic disorders.
Our review explores how environmental triggers (diet, stress, alcohol, infections) and microbiota imbalances damage the tight junction proteins (ZO-1, OCLN, CLDNs), weakening gut barrier integrity and initiating this destructive cascade.
The Microbiome–Barrier Connection: A Powerful Alliance
A balanced microbiome produces short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) like butyrate and propionate, as well as anti-inflammatory compounds like indole-3-propionic acid (IPA) and taurine, which support gut lining integrity and immune tolerance.
In metabolic disorders, beneficial bacteria like Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, Bifidobacterium spp., and Akkermansia muciniphila decline—while pro-inflammatory microbes and harmful metabolites like ethanolamine accumulate, directly destabilizing tight junction mRNA via miR-101a activation.
From Gut to Disease: Metabolic, Immune, and Brain Effects
The article highlights the expanding impact of gut barrier dysfunction in:
- Obesity & Type 2 Diabetes: Elevated LPS, reduced SCFAs, insulin resistance
- Cardiovascular Disease: Increased IPA and butyrate levels correlate with improved arterial health
- Neurodegeneration: Microbial toxins crossing the blood-brain barrier
- IBD & IBS: Tight junction loss and immune overactivation
- Autoimmune Diseases: Gluten and dysbiosis accelerating leaky gut in celiac and T1DM
Therapeutic Pathways: Modulating the Microbiome
Our review outlines promising strategies to combat leaky gut by restoring microbial balance and metabolic function:
- Probiotics: Lactobacillus rhamnosus HL-200, Bifidobacterium, A. muciniphila
- Prebiotics: Fructo- and galacto-oligosaccharides (FOS, GOS), acorn, sago
- Synbiotics: Combining probiotic strains with targeted prebiotics
- Postbiotics: Lipoteichoic acid from heat-killed L. paracasei D3.5 (PoZibio) to enhance barrier integrity
- Next-Generation Probiotics (NGPs): F. prausnitzii, R. intestinalis, and others with metabolic and immune benefits
- Dietary Interventions: Mediterranean and ketogenic diets, taurine, spermidine, metformin
Systems Biology Meets Gut Health: A New Era
Dr. Yadav’s team emphasizes the power of microbiomics + metabolomics—a systems biology approach to identify precise microbial signatures and functional metabolites (e.g., SCFAs, bile acids, IPA) as biomarkers and therapeutic targets for leaky gut and metabolic diseases.
Future therapies could harness AI, personalized microbiome data, and engineered microbes to repair the gut barrier, rebalance immunity, and prevent chronic disease.
Looking Forward: Toward Precision Gut Health
Our review concludes that restoring gut barrier integrity represents a powerful, underutilized strategy to address widespread chronic conditions. Though challenges remain—including lack of diagnostic clarity, regulatory hurdles, and the need for robust clinical trials—emerging microbiome-targeted therapies offer hope for personalized, preventative care.
We're proud to contribute this work from the USF Center for Microbiome Research and to advance the dialogue on how the microbiota–leaky gut–inflammation axis influences lifelong health.
We welcome collaboration with clinicians, researchers, startups, and healthcare innovators interested in developing microbiome-based diagnostics and therapeutics.
🔗 Read the article: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13679-025-00624-0
#Microbiome #LeakyGut #MetabolicHealth #Obesity #Diabetes #PrecisionMedicine #Probiotics #SCFA #GutBrainAxis #MicrobiomeResearch #USF #YadavLab #MusBResearch